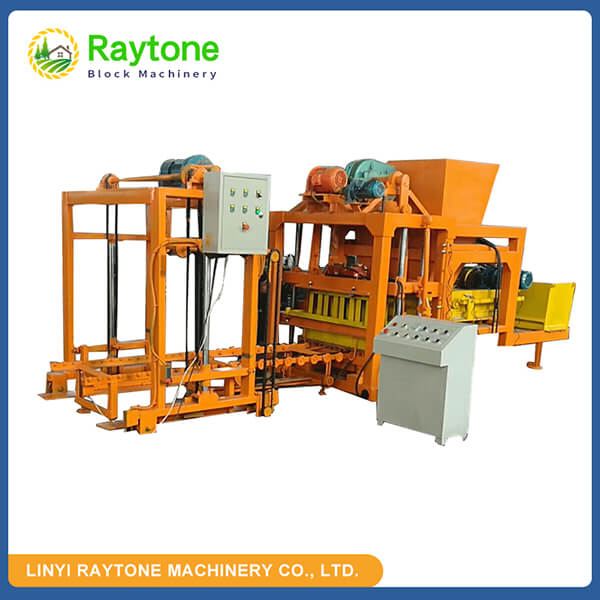
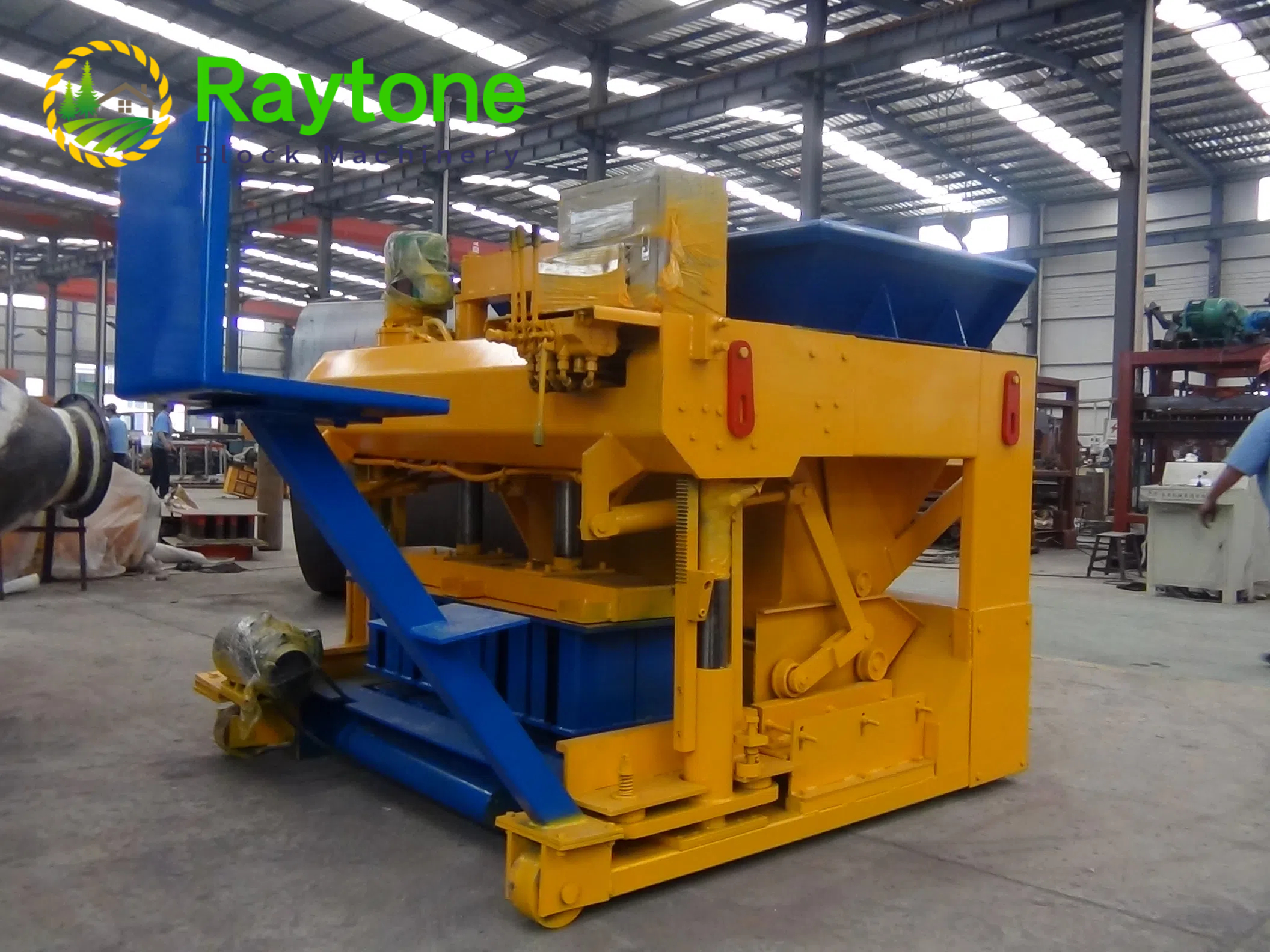
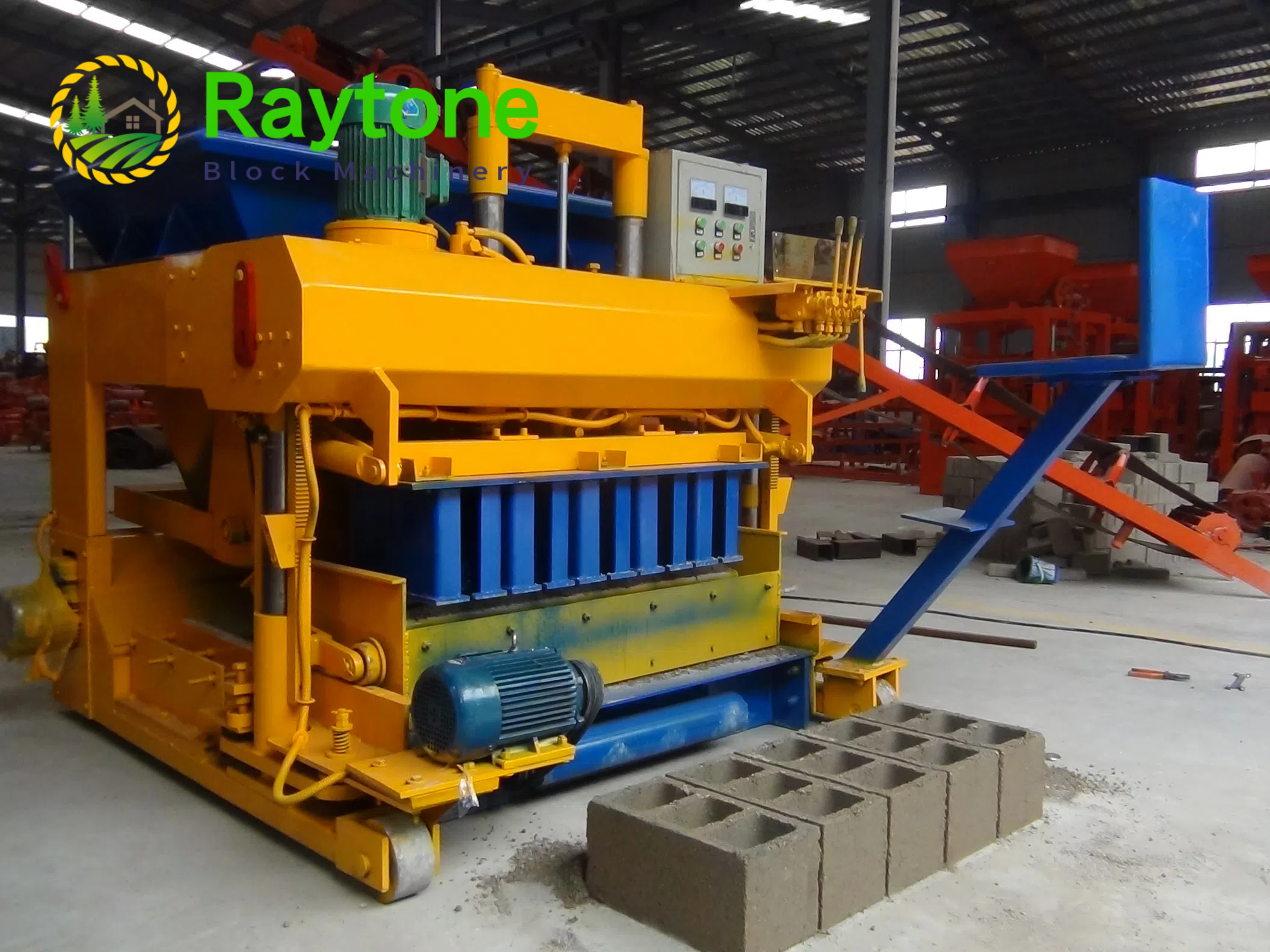
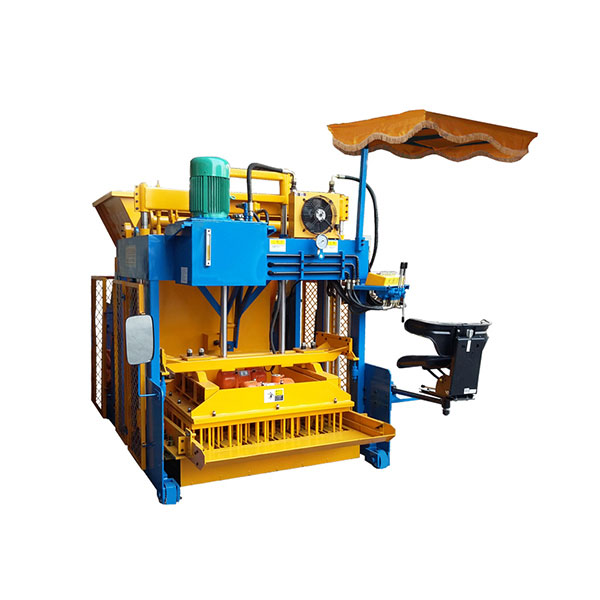
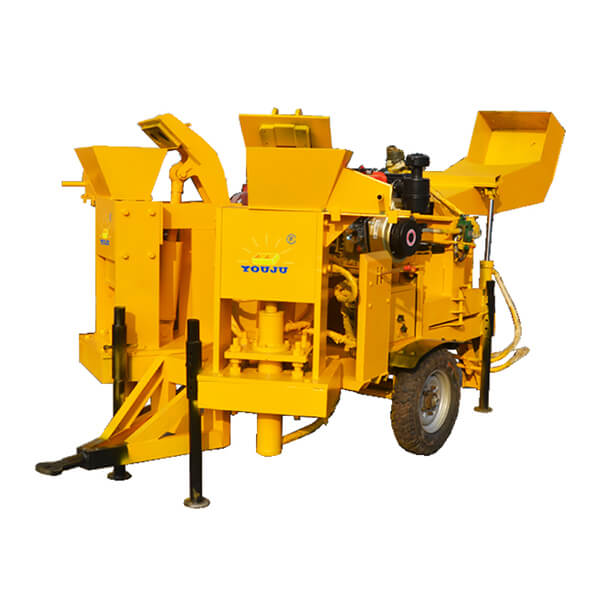
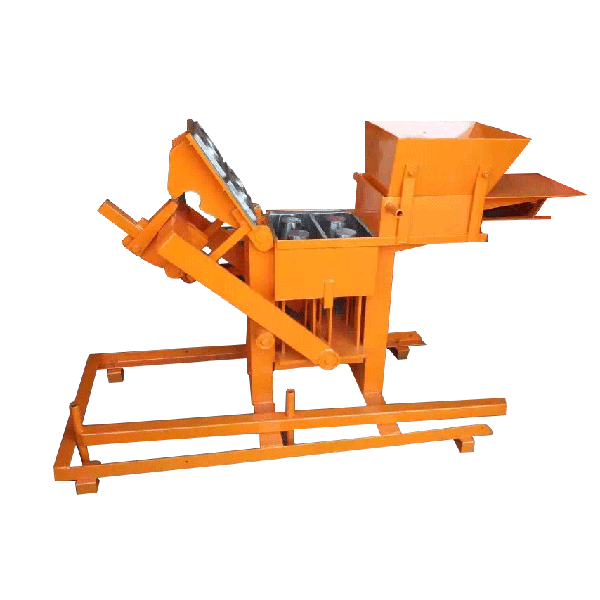
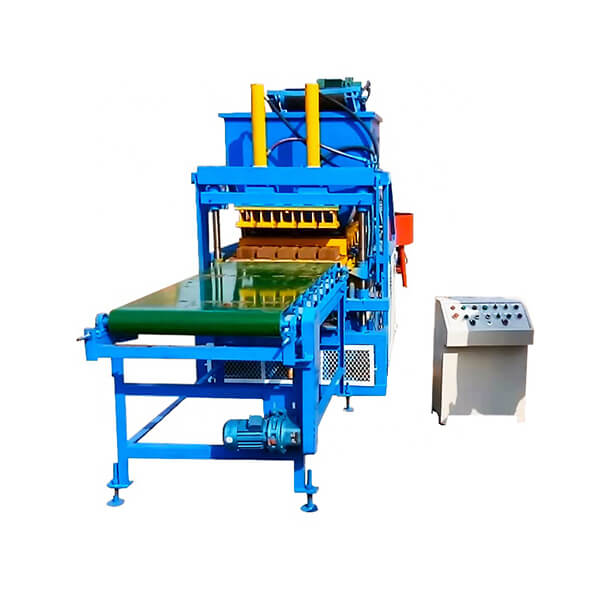
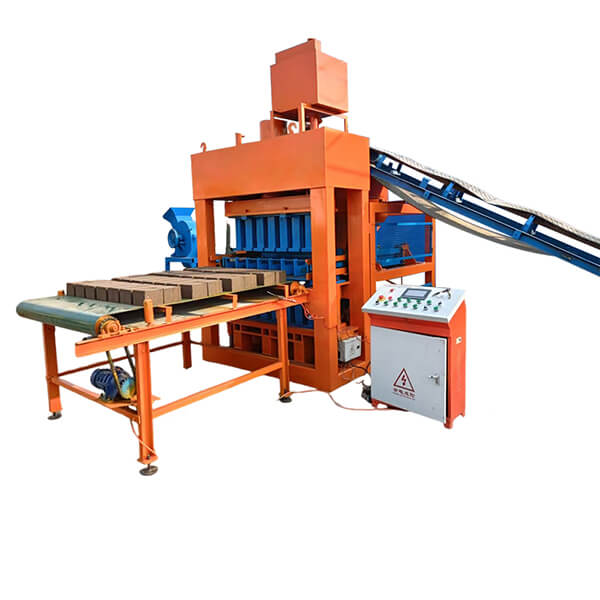
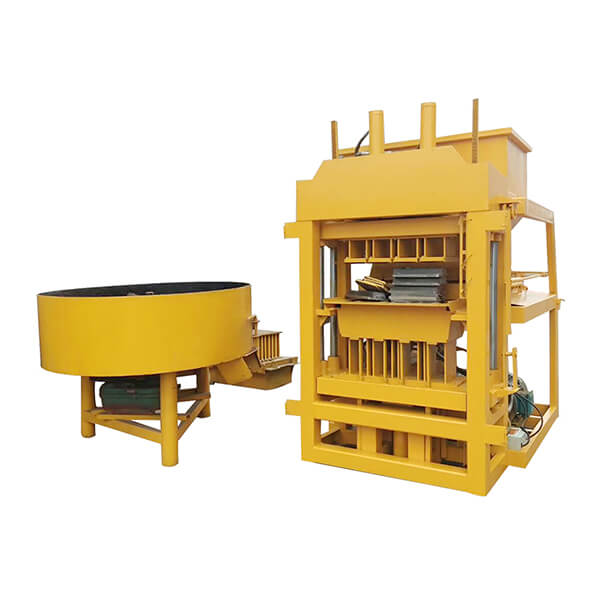
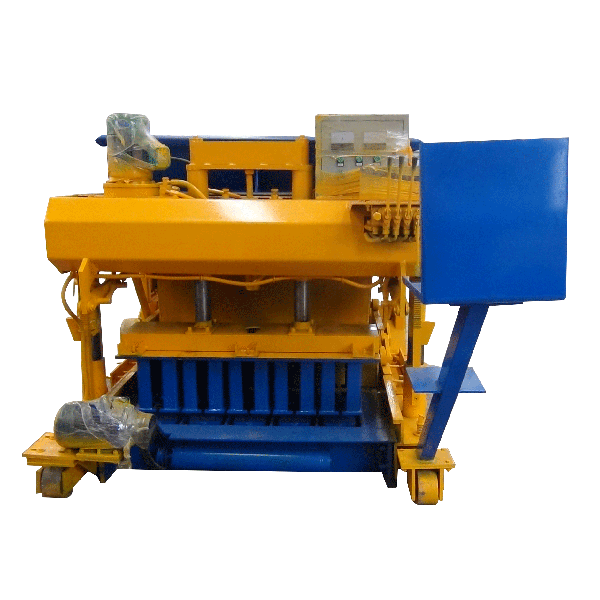
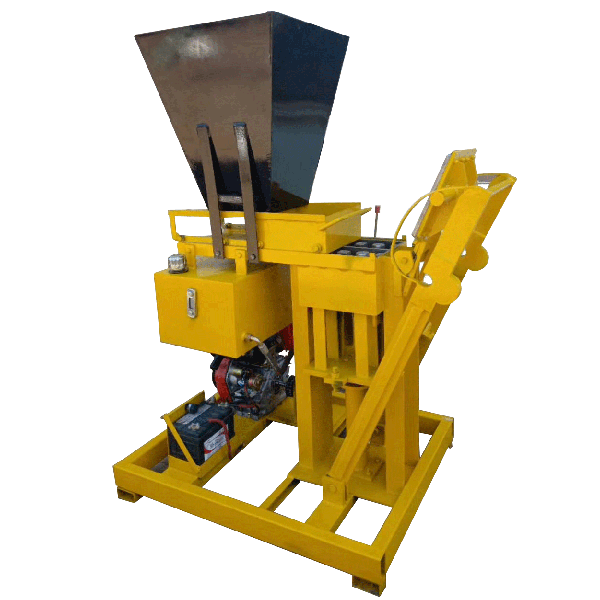
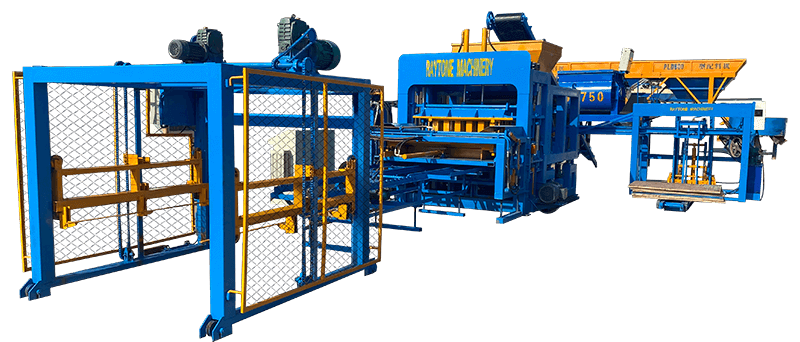
The installation process for the QT4-10 automatic clay brick making machine involves several key steps to ensure optimal performance and longevity. First, a solid foundation is prepared to support the machine’s weight and vibrations. Next, the main components are carefully positioned and aligned, including the hydraulic system, PLC control panel, and brick-forming molds. Proper electrical and hydraulic connections are then established. The raw material feeding system and conveyor belts are installed and calibrated. Finally, the machine undergoes thorough testing and fine-tuning to ensure all systems function correctly. This meticulous installation process, typically carried out by experienced technicians, is crucial for maximizing the efficiency and output quality of this advanced clay brick production equipment.

Preparation and Site Requirements for QT4-10 Machine Installation
Assessing the Installation Area
Before initiating the installation of a QT4-10 automatic clay brick making machine, it’s crucial to carefully assess the designated area. The site should be spacious enough to accommodate not only the machine itself but also allow for efficient material flow and worker movement. Ideally, the installation area should be level, dry, and free from any obstructions that could interfere with the machine’s operation or maintenance.
Additionally, consider the proximity to raw material storage and the finished product storage area. Easy access for loading and unloading materials can significantly enhance the overall efficiency of your brick production process. It’s also wise to factor in future expansion possibilities, leaving some extra space around the machine for potential upgrades or additional equipment.
Foundation Requirements
The foundation for a QT4-10 automatic clay brick machine is a critical component that often gets overlooked. A properly constructed foundation not only supports the weight of the machine but also absorbs vibrations, ensuring stable operation and prolonging the equipment’s lifespan.
Typically, a reinforced concrete foundation is recommended. The exact specifications will depend on the machine’s dimensions and weight, as well as local soil conditions. It’s advisable to consult with a structural engineer to determine the optimal foundation design. The foundation should be level, with a maximum tolerance of 5mm across the entire surface to ensure the machine’s proper alignment.
Electrical and Hydraulic Preparations
The QT4-10 fully automatic clay brick plant relies on both electrical power and hydraulic systems for its operation. Therefore, adequate electrical supply must be available at the installation site. This usually involves a three-phase power supply with the correct voltage and amperage to meet the machine’s requirements.
For the hydraulic system, ensure that high-quality hydraulic oil is available for the initial fill and subsequent maintenance. The area should also have proper drainage systems in place to manage any potential oil leaks or spills, adhering to environmental safety standards.
It’s crucial to have a qualified electrician review your electrical setup and make any necessary upgrades before the machine arrives. This proactive approach can prevent delays and ensure a smooth installation process.
Step-by-Step Installation Guide for the QT4-10 Automatic Clay Brick Machine
Unloading and Positioning the Machine
The first step in installing your QT4-10 automatic clay brick machine is carefully unloading it from the transport vehicle. This process requires heavy-duty lifting equipment, typically a crane or forklift, capable of safely handling the machine’s substantial weight. It’s crucial to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for lifting points to prevent any damage to the equipment.
Once unloaded, the machine should be positioned on the prepared foundation according to the layout plan. Use precision measuring tools to ensure the machine is perfectly level and aligned. Even slight misalignments can lead to operational issues and increased wear on components over time.
Assembling Major Components
With the main body of the QT4-10 fully automatic clay block machine in place, the next step is to assemble and install its major components. This typically includes the hydraulic system, PLC control panel, brick-forming molds, and material feeding system.
The hydraulic system, which is crucial for the machine’s pressing function, needs to be carefully connected and filled with the appropriate hydraulic fluid. The PLC control panel should be mounted in an easily accessible location, protected from dust and moisture.
The brick-forming molds, a key component of the automatic clay brick machine, require precise installation to ensure consistent brick quality. Each mold should be securely fastened and aligned with the pressing mechanism.
Electrical and Hydraulic Connections
Once all major components are in place, it’s time to establish the electrical and hydraulic connections. This is a critical phase that should be carried out by qualified professionals to ensure safety and proper functionality.
The electrical connections involve wiring the control panel to the various motors, sensors, and other electrical components of the machine. It’s essential to follow the wiring diagram provided by the manufacturer meticulously.
For the hydraulic system, all hoses and fittings must be securely connected, ensuring there are no leaks. After connections are made, the system should be bled to remove any air pockets that could affect performance.
Once all connections are complete, it’s crucial to double-check every connection before powering up the machine for the first time. This careful approach can prevent potential damage and ensure a smooth start-up process.
Post-Installation Procedures and Quality Assurance
Initial Testing and Calibration
After the QT4-10 automatic clay brick making machine is fully assembled and connected, the next crucial step is initial testing and calibration. This process begins with a thorough inspection of all components to ensure they are correctly installed and secured.
The testing phase typically starts with running the machine without raw materials. This allows technicians to check the functionality of all moving parts, hydraulic systems, and control mechanisms. They’ll verify that all sensors are working correctly and that the PLC system is communicating effectively with all parts of the machine.
Once the dry run is successful, the next step is to calibrate the machine. This involves adjusting various parameters such as pressing pressure, mold filling time, and conveyor speeds. The goal is to optimize these settings for the specific type of clay and brick design you’ll be producing.
Production Trial and Quality Control
With the machine calibrated, it’s time to conduct a production trial. This involves running a small batch of bricks through the entire production process. During this trial, operators and technicians closely monitor every stage of production, from material feeding to brick forming and ejection.
Quality control is paramount during this phase. Each brick produced should be carefully inspected for consistency in size, shape, and density. Any deviations from the desired specifications should be noted and addressed by further fine-tuning of the machine settings.
It’s not uncommon to run several production trials, adjusting settings each time until the output consistently meets your quality standards. This process, while time-consuming, is crucial for ensuring that your fully automatic clay brick plant is optimized for your specific production needs.
Operator Training and Safety Procedures
The final, yet crucial, step in the installation process is comprehensive operator training. Even the most advanced automatic clay block machine requires skilled operators to run efficiently and safely.
Training should cover all aspects of machine operation, from startup procedures to shutdown protocols. Operators need to understand how to monitor the production process, interpret the control panel readings, and make necessary adjustments during operation.
Equally important is training on safety procedures. This includes proper use of personal protective equipment, emergency shutdown procedures, and routine maintenance tasks. Operators should be well-versed in identifying potential issues before they become serious problems.
It’s advisable to have the machine manufacturer or their representative conduct this training. They can provide insights into the machine’s specific features and best practices for optimal operation. Remember, well-trained operators are key to maximizing the efficiency and longevity of your QT4-10 automatic clay brick making machine.
Conclusion
The installation process for the QT4-10 automatic clay brick making machine is a complex but manageable task when approached systematically. From site preparation and foundation work to the final calibration and operator training, each step plays a crucial role in ensuring the machine’s optimal performance. By following this comprehensive guide, manufacturers can set up their automatic clay brick machine efficiently, paving the way for high-quality brick production. Remember, proper installation is the foundation for years of reliable operation, making it a worthwhile investment of time and resources.
Contact Us
Are you ready to revolutionize your brick production with the QT4-10 automatic clay brick making machine? At Raytone Machinery, we’re committed to providing not just top-quality equipment, but also exceptional support throughout the installation process and beyond. Our team of experts is ready to guide you every step of the way, ensuring your machine is set up for optimal performance and longevity. Experience the difference of working with a leading manufacturer in block-making solutions. Contact us today at hazel@raytonechina.com to learn more about our products and how we can help streamline your brick production process.
References
- Johnson, R. (2022). Advanced Techniques in Clay Brick Manufacturing. Industrial Engineering Quarterly, 45(3), 78-92.
- Smith, A. & Brown, T. (2021). Installation Best Practices for Automated Brick Making Machines. Construction Technology Review, 18(2), 112-126.
- Zhang, L. et al. (2023). Optimizing Clay Brick Production: A Comprehensive Guide. Journal of Building Materials, 56(4), 301-315.
- Miller, K. (2020). Safety Protocols in Automated Brick Manufacturing. Industrial Safety Magazine, 32(1), 45-58.
- Thompson, E. (2022). Quality Control in Clay Brick Production: From Raw Materials to Finished Products. Construction Quality Assurance, 28(3), 201-215.
- Davis, M. & Lee, S. (2021). Energy Efficiency in Modern Brick Making: A Case Study of the QT4-10 Machine. Sustainable Manufacturing Journal, 14(2), 89-103.