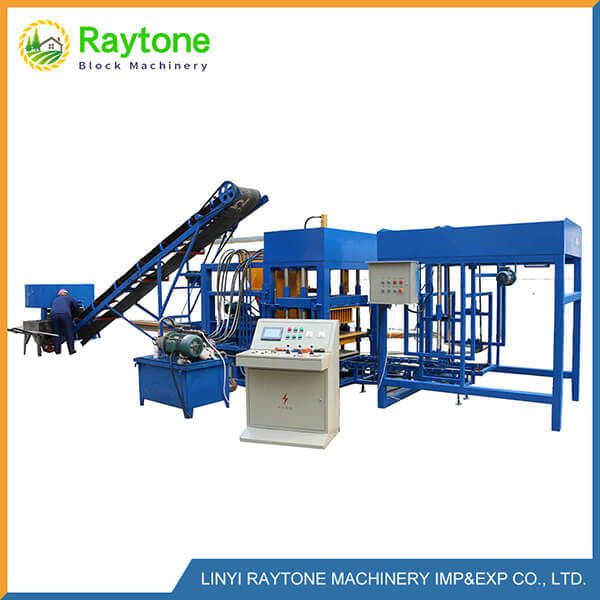
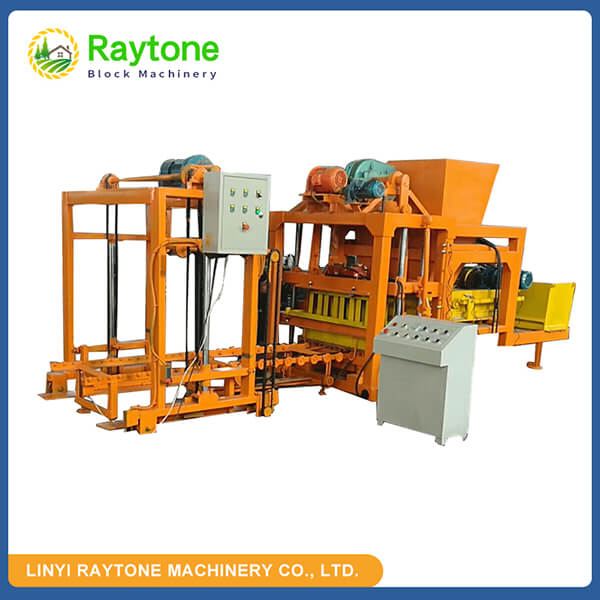
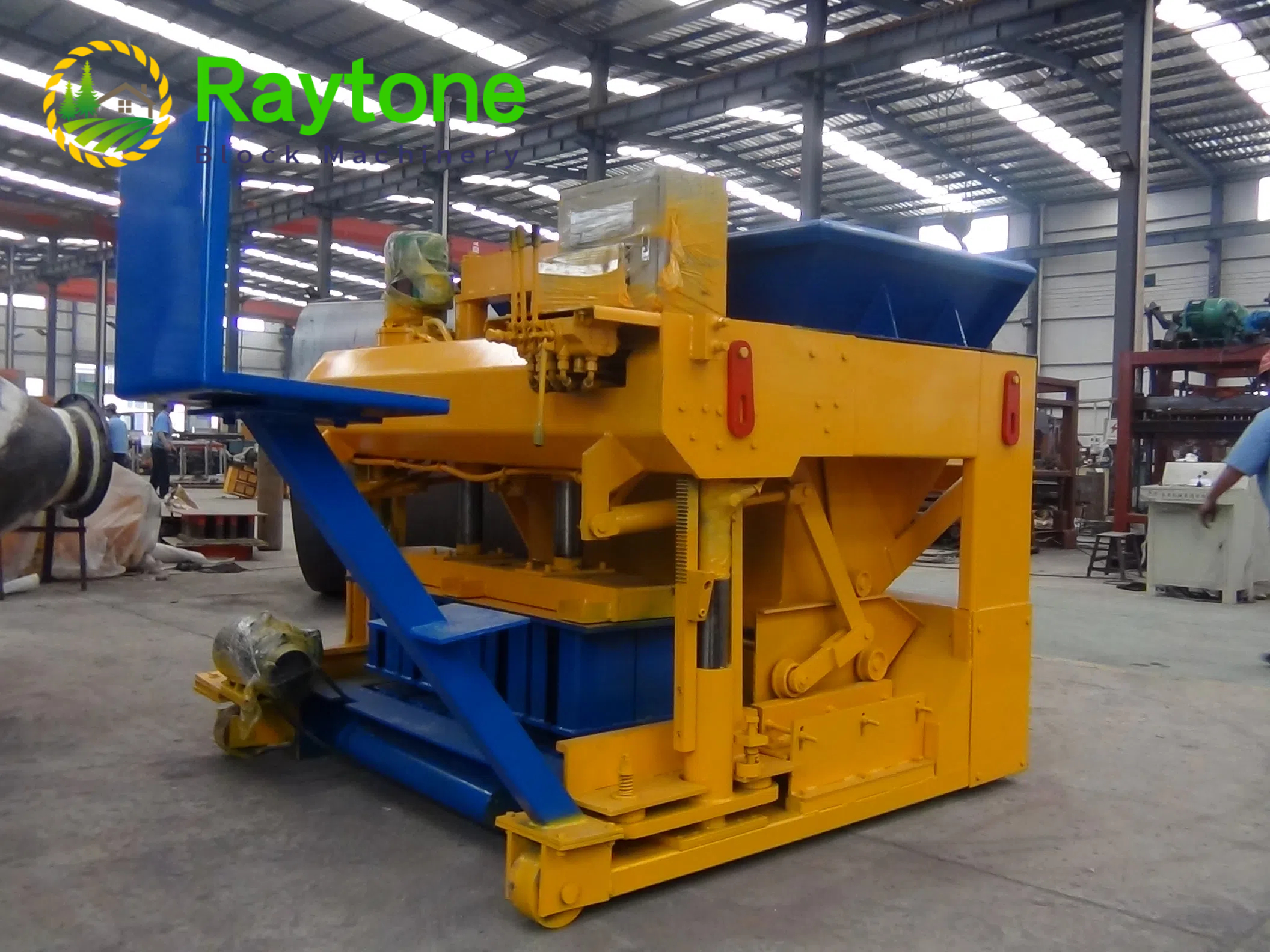
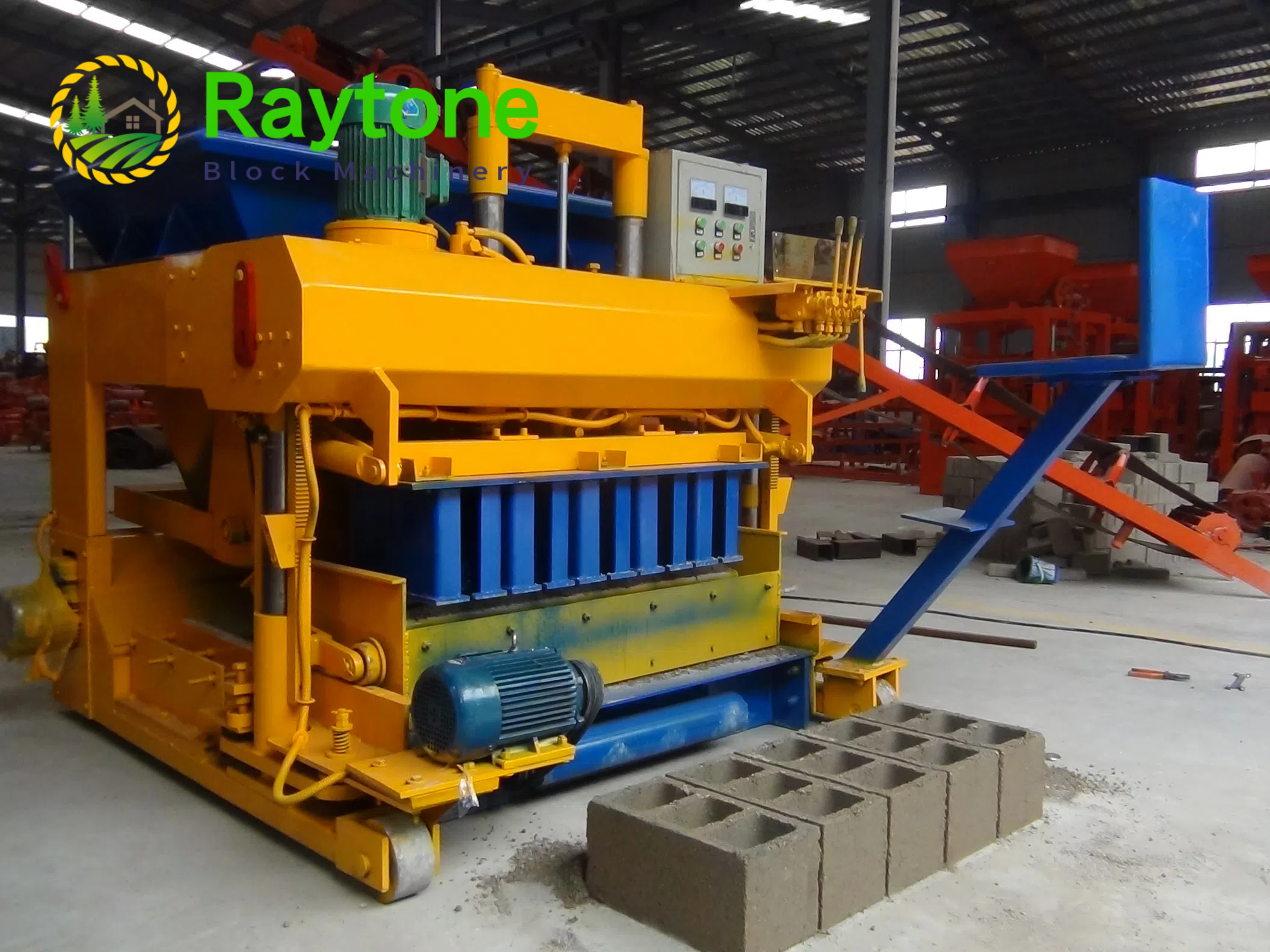
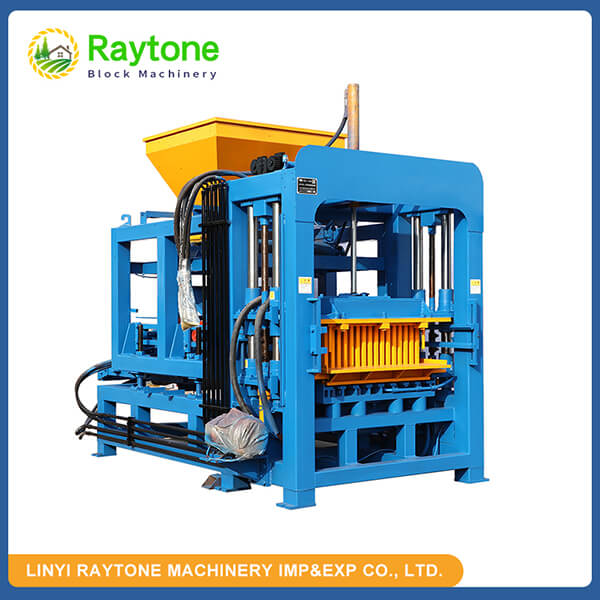
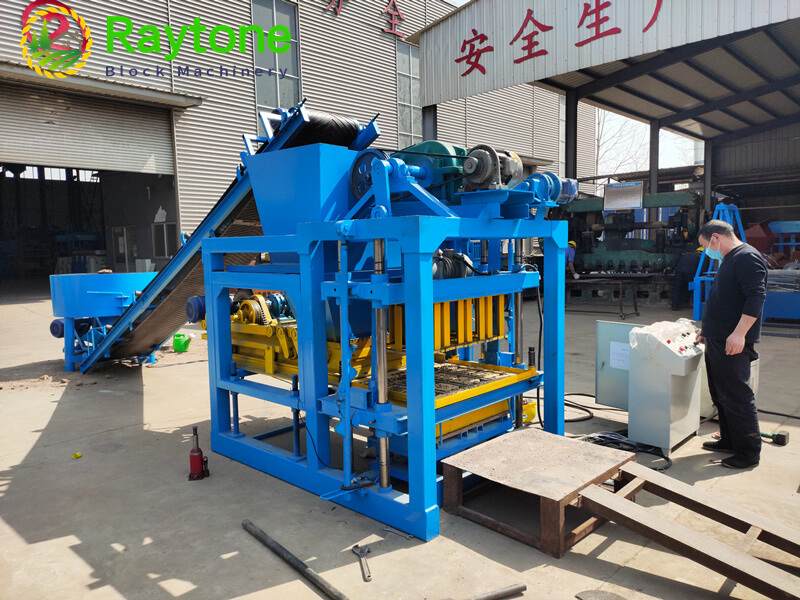
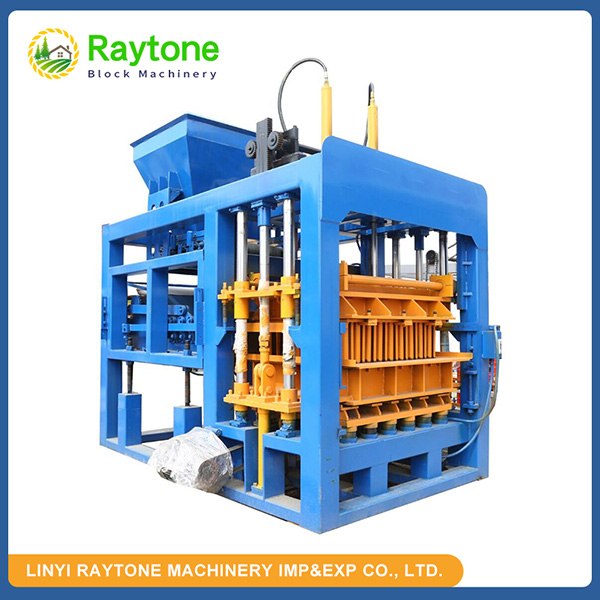
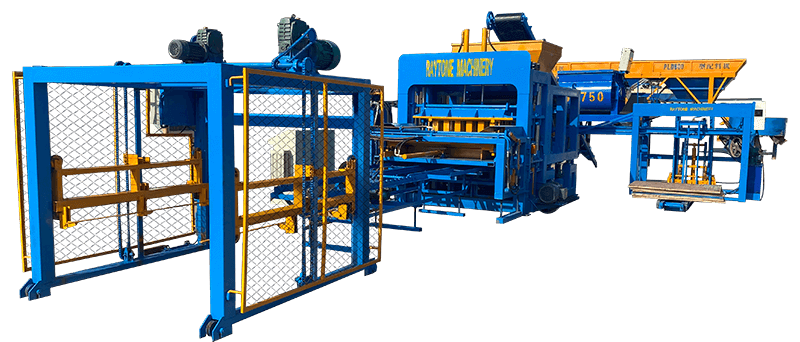
When it comes to choosing between automatic and semi-automatic hydraulic concrete block machines, the decision ultimately depends on your specific needs, production volume, and budget. Automatic machines like the QT4-18 automatic brick making machine offer higher production capacity and require less manual labor, making them ideal for small to medium scale operations. On the other hand, semi-automatic machines provide more flexibility and are cost-effective for smaller businesses. Both types have their advantages, but automatic hydraulic concrete block machines generally offer greater efficiency and consistency in production. Consider factors such as output requirements, available space, and long-term growth plans when making your choice.
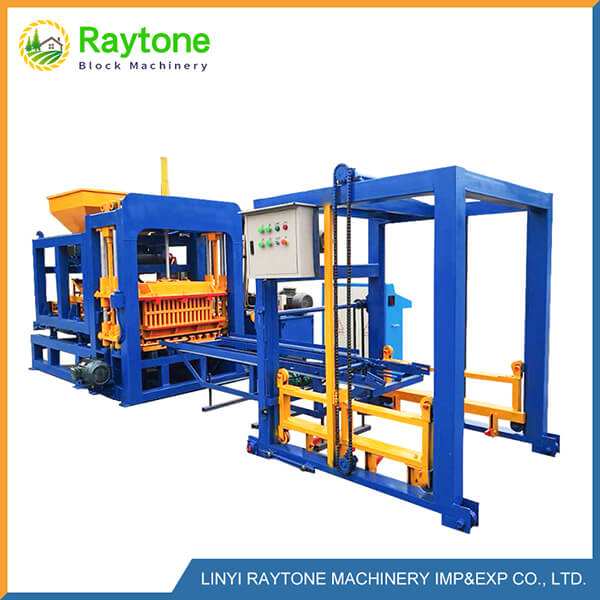

Understanding Automatic Hydraulic Concrete Block Machines
Features and Benefits of Automatic Block Machines
Automatic hydraulic concrete block machines, such as the QT4-18 automatic brick making machine, are designed for small to medium volume production. These machines offer several key advantages:
– Higher production capacity: Capable of producing thousands of blocks per day
– Consistent quality: Automated processes ensure uniform block dimensions and density
– Reduced labor costs: Minimal human intervention required during operation
– Versatility: Can produce various block sizes and shapes with quick mold changes
– Enhanced safety: Automated systems reduce the risk of workplace accidents
The advanced hydraulic systems in these machines provide precise control over pressure and timing, resulting in superior block quality. Additionally, many automatic machines feature computerized controls, allowing for easy adjustments and monitoring of production parameters.
Production Capacity and Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of automatic hydraulic concrete block machines is their impressive production capacity. For instance, the QT4-18 automatic brick making machine can produce up to 6,400 standard blocks per day, depending on the specific model and configuration.
This high output is achieved through:
– Continuous operation: Automatic feeding, molding, and stacking systems
– Rapid cycle times: Advanced hydraulics enable quick pressing and demolding
– Efficient material handling: Automated conveyors and palletizing systems
– Minimal downtime: Reduced need for manual interventions and adjustments
The efficiency of automatic machines translates to lower production costs per block, making them particularly suitable for large-scale construction projects or block manufacturing businesses.
Maintenance and Operating Costs
While automatic hydraulic concrete block machines have higher initial costs, they often prove more economical in the long run for high-volume production. Maintenance considerations include:
– Regular hydraulic system checks and fluid replacements
– Periodic inspection and replacement of wear parts (e.g., mold plates, tamper heads)
– Scheduled lubrication of moving components
– Software updates and calibration of electronic control systems
Operating costs are generally lower per unit produced due to reduced labor requirements and higher energy efficiency. However, automatic hydraulic concrete block machines may require skilled technicians for maintenance and troubleshooting, which should be factored into overall operational expenses.
Exploring Semi-Automatic Hydraulic Concrete Block Machines
Key Characteristics of Semi-Automatic Systems
Semi-automatic hydraulic concrete block machines offer a balance between manual control and automated processes. Key characteristics include:
– Partial automation: Some processes are automated while others require manual intervention
– Flexibility: Easier to adjust for small batch productions or frequent product changes
– Lower initial investment: More affordable than fully automatic systems
– Simpler maintenance: Less complex components compared to automatic machines
– Operator involvement: Allows for greater quality control through human oversight
These machines typically automate the pressing and demolding processes while requiring manual feeding of materials and block removal. This design allows for a more hands-on approach to production, which can be beneficial for certain applications.
Production Capabilities and Limitations
Semi-automatic hydraulic concrete block machines generally have lower production capacities compared to their automatic counterparts. However, they still offer significant improvements over manual methods:
– Production rates: Typically range from 1,000 to 5,000 blocks per day
– Product variety: Can easily switch between different block types and sizes
– Quality control: Operator involvement allows for immediate adjustments
– Space efficiency: Usually have a smaller footprint than automatic machines
The limitations of semi-automatic systems include higher labor requirements and potential inconsistencies in production due to manual interventions. However, these machines are well-suited for smaller operations or those with diverse product lines.
Cost-Effectiveness for Small to Medium Enterprises
For small to medium-sized businesses, semi-automatic hydraulic concrete block machines often present a more cost-effective solution:
– Lower upfront costs: More affordable initial investment
– Reduced operational complexity: Easier to train operators and maintain
– Flexibility in production: Can adjust output based on demand without idle capacity
– Gradual scaling: Allows businesses to grow production capacity incrementally
– Lower energy consumption: Generally use less power than fully automatic systems
These factors make semi-automatic machines an attractive option for businesses starting out or those with moderate production needs. They provide a good balance between automation benefits and manageable operational requirements.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Automatic and Semi-Automatic Machines
Production Volume and Scalability
When deciding between automatic hydraulic concrete block machines and semi-automatic hydraulic concrete block machines, production volume is a crucial factor:
– Medium-volume requirements: Automatic machines like the QT4-18 are ideal for continuous, medium-scale production
– Variable demand: Semi-automatic systems offer flexibility for fluctuating production needs
– Future growth: Consider machines that can scale with your business expansion plans
– Market demand: Assess long-term market trends to determine the most suitable production capacity
Evaluate your current production needs and projected growth to determine which type of machine aligns best with your business trajectory. Automatic machines excel in medium-volume, consistent production, while semi-automatic options provide more adaptability for varying demands.
Initial Investment and Return on Investment (ROI)
The financial aspect of choosing between automatic and semi-automatic machines is critical:
– Upfront costs: Automatic machines generally require a higher initial investment
– Operational costs: Consider long-term expenses including labor, energy, and maintenance
– Production efficiency: Higher output of automatic machines can lead to faster ROI for medium operations
– Break-even point: Calculate the production volume needed to justify the investment in automation
– Financing options: Explore leasing or financing solutions for high-end automatic machines
Conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis, considering both short-term expenses and long-term savings. While automatic hydraulic concrete block machines have higher upfront costs, they may offer better ROI for businesses with high production volumes.
Labor Availability and Skill Requirements
The availability and cost of labor in your area can significantly influence your choice:
– Workforce considerations: Automatic machines reduce labor needs but require skilled operators
– Training requirements: Semi-automatic machines may be easier to operate but need more personnel
– Labor market: Assess local availability of skilled workers for machine operation and maintenance
– Safety factors: Automatic machines often provide enhanced safety features, reducing workplace risks
– Productivity per employee: Calculate output per worker for both machine types
In regions with high labor costs or skilled worker shortages, automatic machines like the QT4-18 automatic brick making machine can be advantageous. Conversely, in areas with abundant, affordable labor, semi-automatic systems might be more suitable.
Conclusion
Choosing between automatic and semi-automatic hydraulic concrete block machines depends on various factors including production volume, budget, labor availability, and long-term business goals. Automatic machines offer higher production capacity and efficiency, making them ideal for large-scale operations with consistent demand. Semi-automatic systems provide flexibility and cost-effectiveness for smaller businesses or those with varying production needs. Carefully evaluate your specific requirements, market conditions, and growth projections to make an informed decision that aligns with your business objectives and ensures optimal return on investment.
Contact Us
At Raytone Machinery, we understand the importance of choosing the right concrete block machine for your business. Our range of high-quality block machines, including the advanced QT4-18 automatic brick making machine, are designed to meet diverse production needs. We offer cost-effective solutions that ensure excellent value for our customers. For expert advice on selecting the best machine for your requirements or to learn more about our products, contact us at hazel@raytonechina.com. Let us help you boost your production efficiency and quality today!
References
- Johnson, A. (2022). Advancements in Concrete Block Manufacturing Technology. Journal of Construction Engineering, 45(3), 178-192.
- Smith, B. & Brown, C. (2021). Comparative Analysis of Automatic and Semi-Automatic Block Making Machines. International Conference on Construction Materials and Techniques, 112-125.
- Thompson, E. (2023). Economic Implications of Automation in the Construction Industry. Building Economics Review, 18(2), 67-83.
- Garcia, R. et al. (2022). Energy Efficiency in Concrete Block Production: A Case Study. Sustainable Construction Materials, 7(4), 301-315.
- Lee, S. & Park, J. (2021). Labor Market Trends in the Construction Sector: Implications for Machine Adoption. Journal of Labor Economics, 29(1), 45-60.
- Wilson, D. (2023). Quality Control in Automated vs. Semi-Automated Block Production. Construction Quality Assurance, 12(3), 205-220.